Understanding the Model Context Protocol
 Before diving into dynamic tool updates, let’s understand what MCP is and why it matters:
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is a standardized interface that allows AI applicaitons and Agents to: Access external tools , Retrieve resources , Use prompt templates .
MCP follows a client-server architecture: MCP Servers - expose tools, resources, and prompts; MCP Clients - connect to servers and use their capabilities; AI Models - interact with the world through these clients
Spring AI provides a comprehensive implementation of MCP with both client and server components, making it easy to integrate AI capabilities into Spring applications.
Before diving into dynamic tool updates, let’s understand what MCP is and why it matters:
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is a standardized interface that allows AI applicaitons and Agents to: Access external tools , Retrieve resources , Use prompt templates .
MCP follows a client-server architecture: MCP Servers - expose tools, resources, and prompts; MCP Clients - connect to servers and use their capabilities; AI Models - interact with the world through these clients
Spring AI provides a comprehensive implementation of MCP with both client and server components, making it easy to integrate AI capabilities into Spring applications.
The Dynamic Tool Update Feature
One powerful aspects of the MCP is the ability to dynamically update the available tools at runtime. This means:- MCP Servers can add or remove tools without restarting
- MCP Clients can detect these changes
- AI models can immediately use the new capabilities
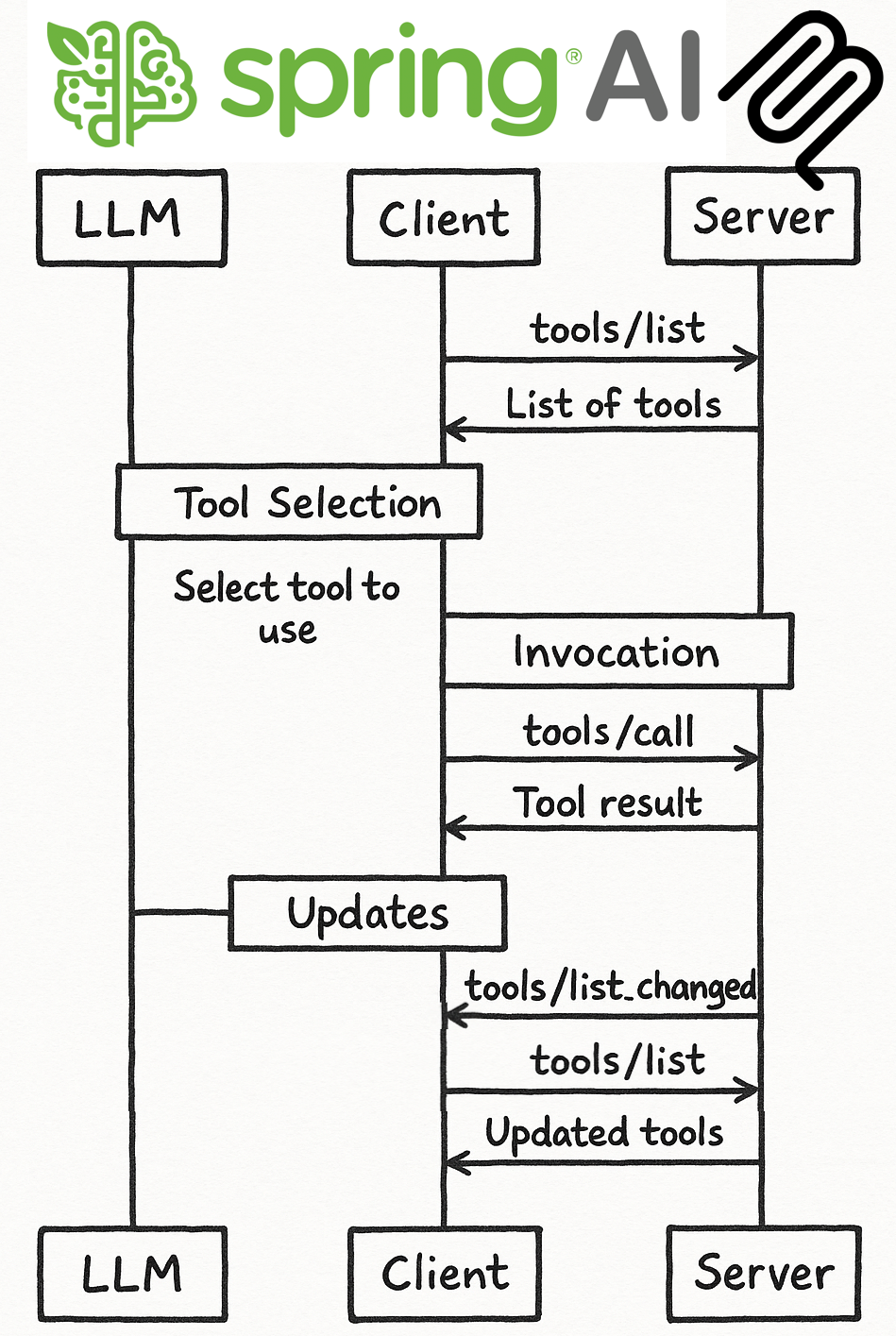
How Dynamic Tool Updates Work
The dynamic tool update process involves several components working together:Server-Side Implementation
Spring AI’s@Tool annotation makes it easy to expose methods as MCP tools:
- Extracts method parameters as tool inputs
- Generates appropriate JSON schemas
- Handles parameter validation and conversion
- The server initially exposes only weather forecast tools
- When a custom tool-update signal is received the
McpSyncServer.addTool()method is used to dynamically register new tools
McpSyncServer class provides methods for tool management:
addTool(SyncToolSpecification)- Adds a new toolremoveTool(String)- Removes a tool by namenotifyToolsListChanged()- Notifies clients about tool changes
NOTE: you can add and/or remove Tools only after the Clinet/Server connection has been initialized.
Client-Side Implementation
The MCP protocol includes a notification system that allows servers to inform clients about changes to available tools. This notification system ensures that clients always have an up-to-date view of the server’s capabilities. On the client side, Spring AI provides mechanisms to detect and react to tool changes:- Be notified when tools are added or removed
- Update its internal state accordingly
- Make the new tools immediately available to the AI model
Tool Discovery and Usage
The client can discover available tools at any time:TIP: The client implementation relies on the fact that the ToolCallbackProvider#getToolCallbacks implementation for MCP will always retrieves the current list of MCP tools from the server. This means that whenever a client requests the available tools, it will always get the most up-to-date list from the server, without needing to restart or reinitialize the client.
Practical Applications
Dynamic tool updates in MCP enable several powerful use cases:1. Feature Flags for AI Capabilities
You can implement feature flags that control which AI capabilities are available:2. Context-Aware Tool Loading
Load tools based on the current context or user permissions:3. Progressive Enhancement
Start with basic tools and add more advanced capabilities as needed:4. Dynamic Plugin Architecture
Implement a plugin system where new capabilities can be added at runtime:Conclusion
Spring AI’s handling of dynamic tool updates in the Model Context Protocol provides a mechanism for extending AI capabilities at runtime. This feature enables more flexible, extensible, and resource-efficient AI applications. Key takeaways:- Standardized Interface: MCP provides a consistent way for AI models to interact with external tools and resources.
- Dynamic Updates: Tools can be added or removed at runtime without requiring application restarts.
- Automatic Discovery: Clients can detect changes to available tools and make them immediately available to AI models.
- Simple API: Spring AI provides a clean, annotation-based API for defining and managing MCP tools.