1. Function Calling in Java
If you want to test out the latest Mistral AI features using Java and Spring AI, you will find that Mistral doesn’t support Java clients and hasn’t released the Function Calling API yet. Consequently, I had to resort exploring their JavaScript/Python clients to to figure it out. Below, is a class diagram illustrating the various components of the API and their interconnections.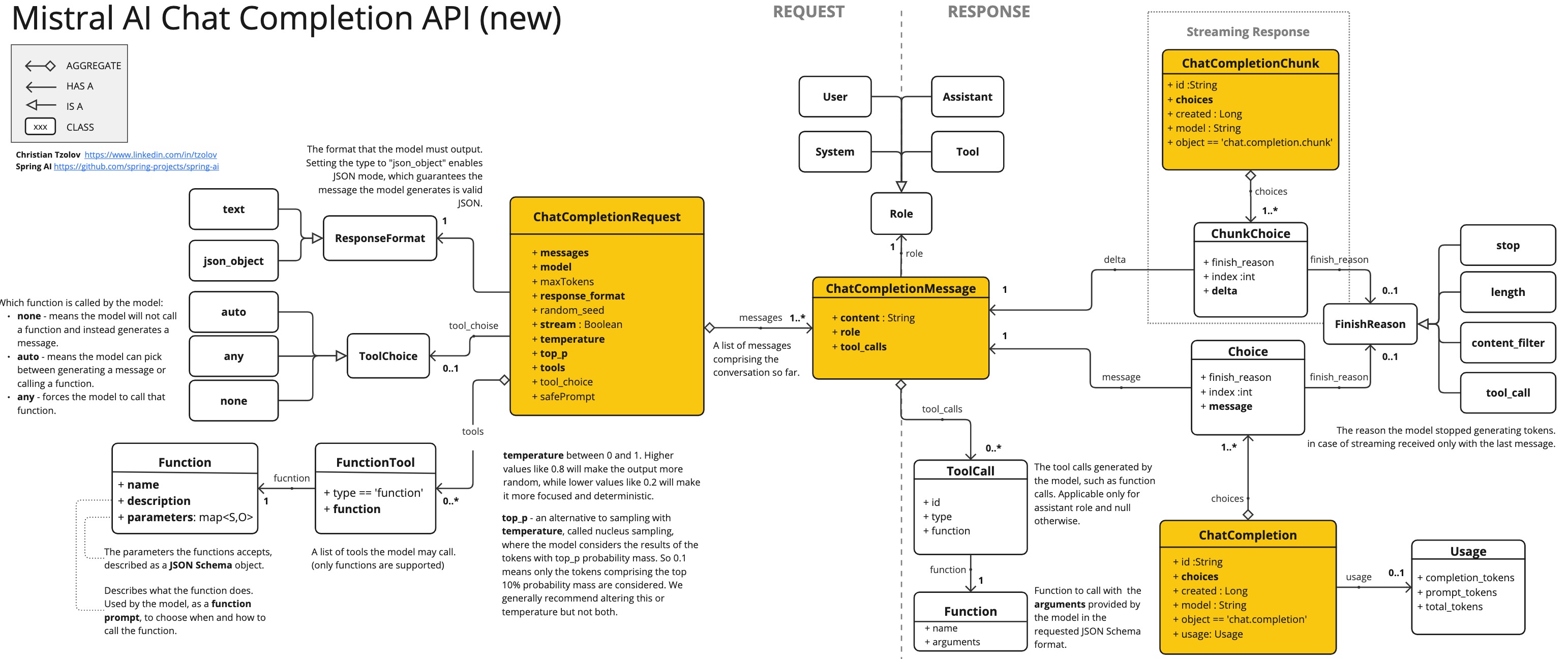 Those familiar with the OpenAI API will notice that Mistral AI’s new API is almost the same, with just a few small differences.
I’ve extended the MistralAiApi Java client, originally created by Ricken Bazolo, to include the missing Function Calling features.
The updated client works well, as demonstrated by the Payment Status demo.
Since my focus is on Spring AI, I won’t delve into the technical intricacies of the client here. However, if you’re interested, you can explore the demo code and the cheat sheet diagram I’ve included below.
Those familiar with the OpenAI API will notice that Mistral AI’s new API is almost the same, with just a few small differences.
I’ve extended the MistralAiApi Java client, originally created by Ricken Bazolo, to include the missing Function Calling features.
The updated client works well, as demonstrated by the Payment Status demo.
Since my focus is on Spring AI, I won’t delve into the technical intricacies of the client here. However, if you’re interested, you can explore the demo code and the cheat sheet diagram I’ve included below.
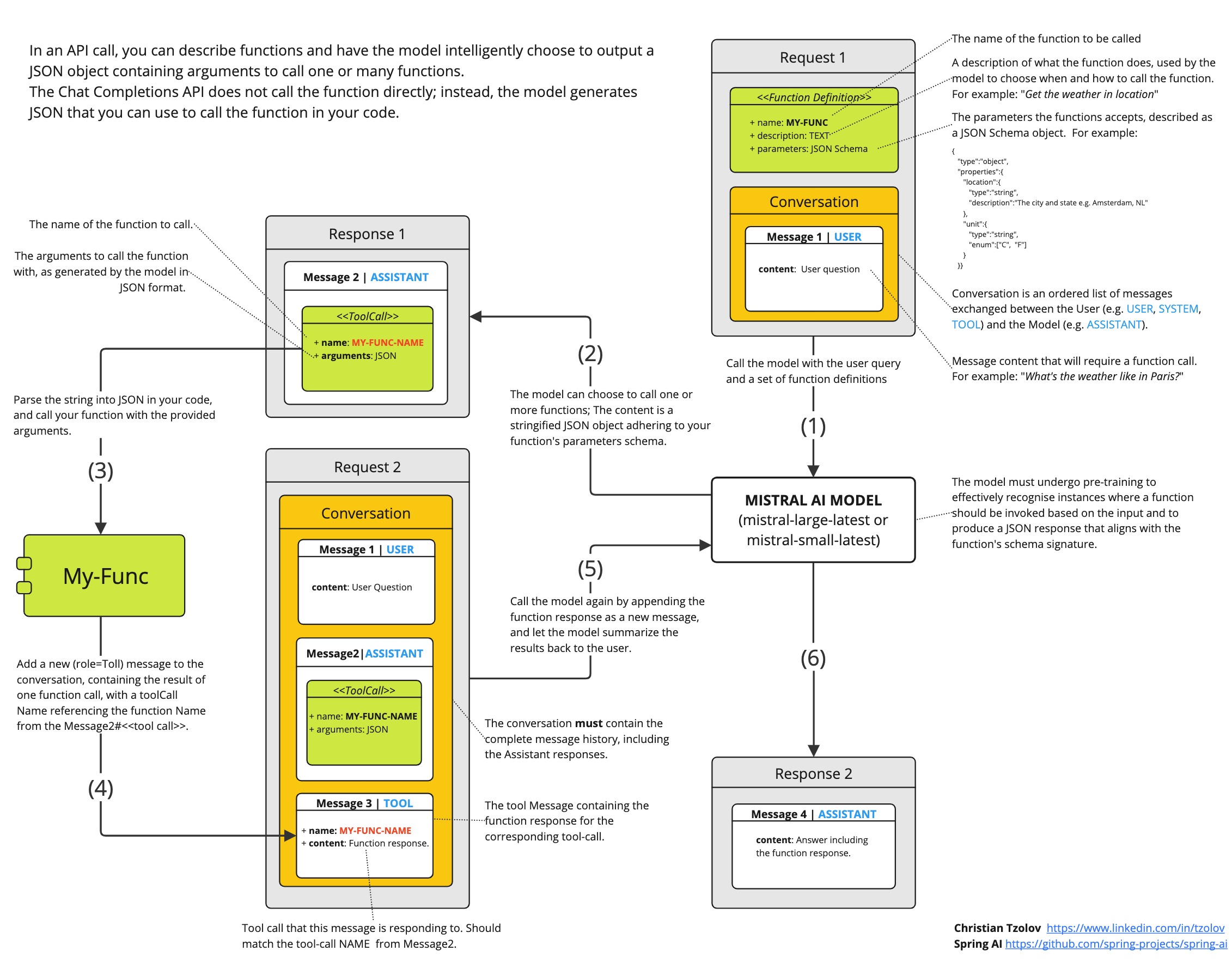 It’s important to note that the model doesn’t directly call the function; rather, it generates JSON for you to call the function in your code and return the result to the model to continue the conversation.
It’s important to note that the model doesn’t directly call the function; rather, it generates JSON for you to call the function in your code and return the result to the model to continue the conversation.
2. Function Calling with Spring AI
Spring AI simplifies Function Calling by allowing you to define a@Bean that returns a user-defined java.util.Function. It automatically infers the Function’s input type and generates JSON (or Open API) schema accordingly. Moreover, Spring AI takes care of the complex interactions with the AI Model by wrapping your POJO (the function) with the necessary adapter code, eliminating the need for you to write repetitive code.
Furthermore, the Spring AI simplifies the code portability to other AI models that support Function Calling and allows the development of efficient, native (GraalVM) executables.
2.1 How does it work?
Suppose we want the AI model to respond with information that it does not have. For example the status of your recent payment transactions as shown in this Mistral AI tutorial. Lets re-implement the tutorial with Spring AI. Bootstrap a new Boot application using the Initializr and add the MistralAI boot starter dependency to the POM:application.properties to configure it:
MistralAiChatClient:
java.util.Function that takes a Transaction as an input and returns the Status for that transaction.
Function is registered as @Bean and uses the @Description annotation to define function description.
Spring AI greatly simplifies code you need to write to support function invocation.
It brokers the function invocation conversation for you.
You can also reference multiple function bean names in your prompt.
TIP: Rather than repeatedly specifying the function name in prompt options for each request, you can consider configuring it once in theThat’s it. Spring AI will facilitate the conversation for function invocation on your behalf. You can print the response content:application.propertiesfile like:spring.ai.mistralai.chat.options.functions=retrievePaymentStatus. This approach ensures the function is consistently enabled and accessible for all prompt questions. However, it’s important to note that this method may result in the transmission of unnecessary context tokens for requests that do not require the function.
TIP: Check the MistralAi-AOT-Demo, a simple, Spring Boot application showcasing the integration of Mistral AI with Spring AI. It encompasses various functionalities such as chat completion, streaming chat completion, embedding, and function calling. Additionally, instructions for native builds are included.Explore further details about the integration of Spring AI with Mistral AI in the reference documentation:
2.2 Dynamic Prompt Options
With MistralAiChatOptions, we can customize the default settings for each prompt request. For instance, we can switch the model to LARGE and adjust the temperature for a specific request as needed.:2.3 Code Portability
Porting the code to other models supporting function calling is straightforward. For instance, to transition the code from using Mistral AI to Azure OpenAI, follow these steps:- Replace the
spring-ai-mistral-ai-spring-boot-starterdependency withspring-ai-azure-openai-spring-boot-starter. - Adjust the
application.propertiesfile: - Rename the
MistralAiChatOptionsclass toAzureOpenAiChatOptions(this renaming may become unnecessary in future Spring AI versions).
3. Build Native (GraalVM) Execution
For building a native image you need to install a GrallVM 21 JDK and runt the following maven command:4. Conclusions
In this blog post we explore the Mistral AI Function Calling features in conjunction with Java and Spring AI. The focus is on leveraging Function Calling with Spring AI, a framework that streamlines the integration process by handling the complexities of interaction with AI models, facilitating code portability and the development of efficient, native (GraalVM) executables. Key points covered include:- Overview of Function Calling with Spring AI, including demos and code examples.
- Explain the dynamic Prompt Options and Code Portability across different AI models supported by Spring AI.
- Building Native (GraalVM) Execution for enhanced performance